
Sleep deprivation is a condition that occurs if you don't get enough sleep. Sleep deficiency is a broader concept. It occurs if you have one or more of the following:
Sleeping is a basic human need, like eating, drinking, and breathing. Like these other needs, sleeping is vital for good health and well-being throughout your lifetime.
According to the Centres for Disease Control and Prevention, about 1 in 3 adults in the United States reported not getting enough rest or sleep every day.
Nearly 40% of adults report falling asleep during the day without meaning to at least once a month.
Sleep deficiency can lead to physical and mental health problems, injuries, loss of productivity, and even a greater likelihood of death. Without enough sleep, your brain and body systems won’t function normally. It can also dramatically lower your quality of life.
You may be sleep deprived if you:
Noticeable signs of sleep deprivation include:
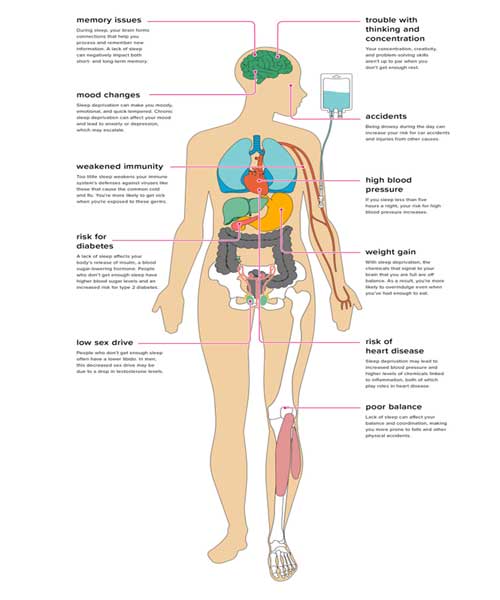
Sleep deprivation can have a wide range of negative effects on various aspects of health and well-being. Here are some common effects of sleep deprivation:
1. Cognitive Impairment:
Lack of sleep can impair cognitive functions such as attention, concentration, reasoning, problem-solving, and memory. It becomes more difficult to learn, retain information, and perform complex mental tasks.
2. Reduced Alertness and Performance:
Sleep deprivation leads to decreased alertness, vigilance, and reaction time. It can impair decision-making abilities, creativity, and problem-solving skills. This can have a significant impact on daily tasks, work, and academic performance.
3. Mood Disturbances:
Sleep deprivation often leads to irritability, mood swings, and an increased risk of developing mood disorders such as depression and anxiety. Emotional regulation becomes more challenging, and individuals may experience heightened emotional reactivity.
4. Increased Risk of Accidents:
Sleep deprivation impairs judgment, attention, and reaction time, increasing the risk of accidents and errors. This is particularly concerning in activities such as driving, operating machinery, or engaging in high-risk occupations.
5. Weakened Immune Function:
Lack of sleep compromises the immune system, making individuals more susceptible to infections, colds, and flu. It can also slow down the healing process and reduce the body's ability to fight off illness.
6. Metabolic Imbalance and Weight Gain:
Sleep deprivation can disrupt hormonal balance, leading to increased appetite, cravings for high-calorie foods, and a higher risk of weight gain and obesity. It is associated with imbalances in hormones related to hunger and satiety, such as ghrelin and leptin.
7. Increased Cardiovascular Risk:
Chronic sleep deprivation is linked to an increased risk of hypertension (high blood pressure), heart disease, and stroke. It can negatively impact blood pressure regulation and contribute to the development of cardiovascular conditions.
8. Impaired Immune Function:
Sleep deprivation weakens the immune system, making individuals more vulnerable to infections, viruses, and diseases. It can lead to prolonged recovery from illnesses and reduced ability to fight off pathogens.
9. Mental Health Issues:
Sleep deprivation is associated with an increased risk of developing mental health conditions, such as depression, anxiety, and mood disorders. It can exacerbate symptoms in individuals with pre-existing mental health conditions.
10. Decreased Quality of Life:
Overall, sleep deprivation significantly impairs the quality of life. It affects physical and mental well-being, reduces energy levels, impairs social interactions, and can lead to feelings of fatigue, exhaustion, and diminished overall functioning.
It's important to prioritize healthy sleep habits and ensure adequate sleep duration to minimize the negative effects of sleep deprivation. If you're experiencing persistent sleep problems or the effects of sleep deprivation, it's advisable to consult with a healthcare professional for proper evaluation and guidance.